Sampling distribution
Published:
This post covers Introduction to probability from Statistics for Engineers and Scientists by William Navidi.
Exercises
A mobile computer network consists of a number of computers (called nodes) that communicate with each other while moving throughout a region. A node that is out of transmission range of the other nodes, so that it is unable to communicate, is said to be partitioned.
In studies, it is found that in a network containing $185$ nodes in which destinations were chosen at random from a uniform distribution, $19$ nodes were partitioned. It is also found that in a network containing $164$ nodes whose movements mimicked those on a college campus, $30$ nodes were partitioned. Find a $99\%$ confidence interval for the difference between the proportions of partitioned nodes in the two networks.
Solution $(−0.0176, 0.1772)$
A mobile computer network consists of computers that maintain wireless communication with one another as they move about a given area. A routing protocol is an algorithm that determines how messages will be relayed from machine to machine along the network, so as to have the greatest chance of reaching their destination. The article
“Performance Comparison of Two Location Based Routing Protocols” compares the effectiveness of two routing protocols over a variety of metrics, including the rate of successful deliveries. Assume that using protocol A, $200$ messages were sent, and $170$ of them, or $85\%$, were successfully received. Using protocol B, $150$ messages were sent, and $123$ of them, or $82\%$, were successfully received.
Find the P-value for the difference between the proportions of rate of successful deliveries.
Solution The P-value is $0.2266$

A mobile ad hoc computer network consists of several computers (nodes) that move within a network area. Often messages are sent from one node to another. When the receiving node is out of range, the message must be sent to a nearby node, which then forwards it from node to node along a routing path toward its destination. We wish to predict the proportion of messages that will be successfully delivered, which is called the goodput.
It is known that the goodput is affected by the average node speed and by the length of time that the nodes pause at each destination. Below table presents average node speed, average pause time, and goodput for 25 simulated mobile ad hoc networks.
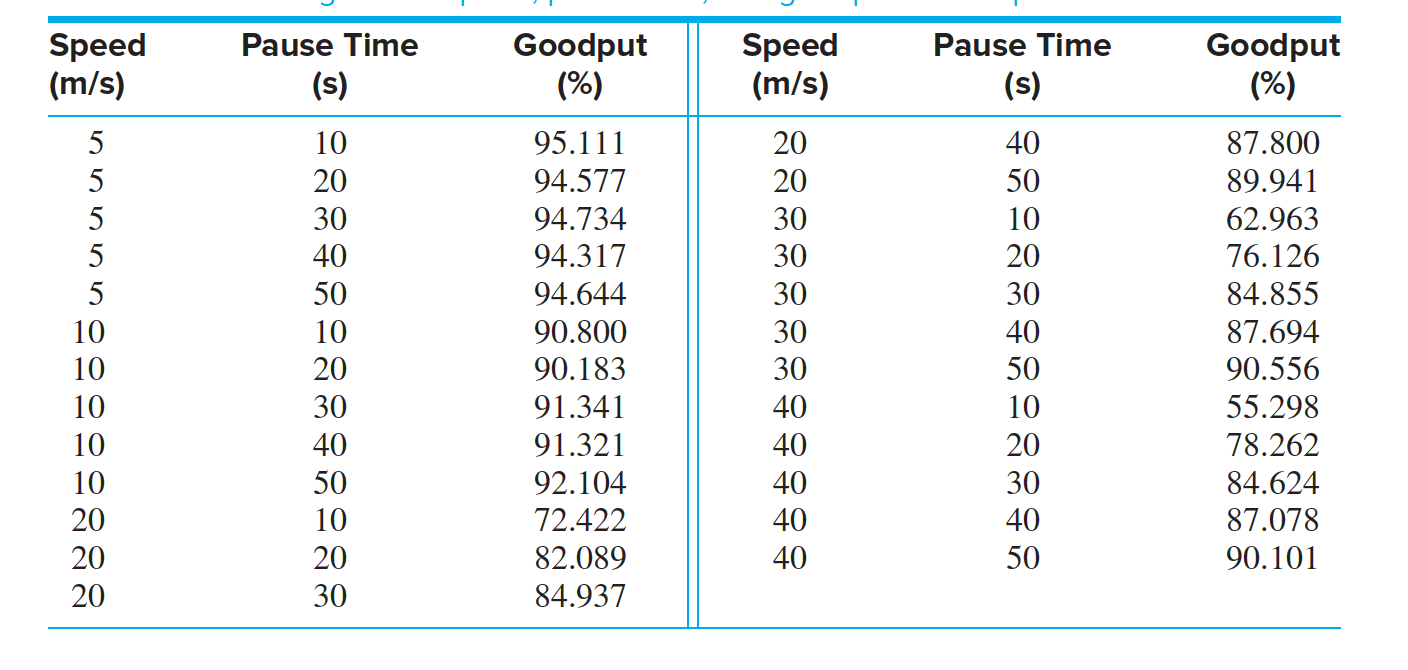
The estimated coefficient for the goodput for a network is −1.8245, with a standard deviation of 0.2376. Find a 95% confidence interval.
Solution (−2.3218, −1.3272)